The Perfect Storm – Part 2
Oil and gas companies are looking at a bonanza from the Ukraine war
Oil and gas companies see new profits and a stay of execution from the Ukraine war. Few in the industry want to admit it, but many fossil fuel interests are leveraging the current supply disruptions created by Russian embargos as the perfect storm – one to justify soaring prices, while engaging in a narrative of panic and self-reaffirming “we told you so” feeding the fears of fuel shortages and fossil fuel dependency.
More than a momentary perfect storm, the fossil fuel industry has been forestalling the overdue day of reckoning when the cost of addiction meets the cost of recovery in what will prove to be a truly titanic struggle.
In part one of the “Perfect Storm” we identified the obvious and less talked about costs of our ongoing fossil fuel dependency, beginning with humans modifying the planet’s climate and environment in the name of energy with disastrous consequences to poisoning humans with deadly health outcomes.
“There is a huge opportunity for oil and gas companies, though I’m sure it is not one they would have chosen,” said Robert Buckley, head of relationship development at Cornwall Insight, an energy analysis company. “They have the opportunity to reposition themselves [as crucial to policymakers]. There is going to be a very high price for oil for a very long time, and even the prospect of physical energy shortages.”
Scientists and climate experts warn that oil and gas companies were using the Ukraine emergency to further their own interests, by encouraging governments to prioritize oil and gas production and make decisions now on investments that would have little impact on the current crisis, but would vastly increase fossil fuel use for years to come and further accelerate global warming.
A stark reminder of the likely consequences of further dependence on oil and gas came from the International Energy Agency, reported Tuesday that greenhouse gas emissions had shown the highest ever annual increase in 2021.
The global energy watchdog found that energy-related carbon dioxide emissions, which make up the bulk of greenhouse gases, had risen by 6% in 2021 to 36.3bn tons, their highest-ever level, as the global economy rebounded from the Covid-19 pandemic, relying heavily on coal to power the growth. The increase in global CO2 emissions was more than 2bn tons, the largest in history in absolute terms, outweighing the decline in emissions seen during the lockdowns of 2020.
Hawaii’s transition to renewables becomes all the more urgent
Overall, the U.S. consumes use very little Russian oil. In 2021, oil from that country represented just 3% percent of total U.S. crude imports and just 1% of the oil processed by U.S. refineries, according to the American Fuel and Petrochemical Manufacturers (AFPM) trade association.
But Hawaii is an outlier among other U.S. states. The state imports several million barrels of Russian crude oil annually, accounting for 10% to 25% of Russian crude shipments to the U.S. depending on the year. As Russia’s invasion of Ukraine rattles energy markets it is also a wake up call for Hawaii’s clean energy ambitions.
Soaring oil prices—the benchmark Brent and U.S. crude futures are up over 15% since Russia invaded neighboring Ukraine last week, touching at least 10-year highs—come at a particularly inconvenient time for the island state. Its coal-powered AES electrical plant in West Oahu, the biggest plant on its most populated island, is set to shutter in September 2022.
The renewable energy projects meant to replace it face a number of utility-led delays and supply-chain setbacks. Extending the life of state’s oil dependency and adding questionable biomass power plants are part of a fallback plan to keep the lights on for Oahu residents.
“We have warned about leaving the cost of this transition up to world oil markets, and this week’s events are another reminder of the price we pay for oil dependence,” Jay Griffin, chair of the Hawaii Public Utilities Commission.
The Russian invasion of Ukraine has also led the United States and its European allies to impose severe economic penalties on Russia.
Par Pacific, the largest operating refinery in Hawaii, announced that it would stop buying Russian crude oil for its Kapolei refinery “in light of recent geopolitical events.” “The geopolitical landscape and energy markets are dynamic. We will continually monitor and evaluate our posture on Russian crude over the coming weeks and months,” the company said in a statement. Par Pacific added that it will look to South America and Canada to help meet fuel production requirements.
Hawaii’s external energy dependences
President Joe Biden announced Tuesday that the U.S. will target “the main artery of Russia’s economy” by banning the import of Russian energy products.” “Putin’s war is already hurting American families at the gas pump,” Biden said. “I’m going to do everything I can to minimize Putin’s price hike here at home.”
Hawaii relies heavily on Russian crude oil and we can expect an outsized share of the pain at the gas pump, specifically impacting the majority of drivers who depend on ICE vehicles for transportation.
“We’re banning all imports of Russian oil and gas and energy,” Biden said. “That means Russian oil will no longer be acceptable at U.S. ports and the American people will deal another powerful blow to Putin’s war machine.”
Oil prices were already up before the President’s announcement as post-Covid consumer demand was outstripping short term supplies. And on again, a familiar pattern can seen in the disruptive nature wars have on oil and gas prices. It’s a pattern that is familiar to historians – a pattern linking modern wars to oil and gas.
In 1940 Japan invaded French Indochina in an effort to embargo all imports into China, including war supplies purchased from the U.S. This move prompted the United States to embargo all oil exports destined for Japan , an action which supported the Imperial Japanese Navy’s global war designs, and provided Japan the perfect excuse to attack Hawaii on December 7th, 1941, which marked the beginning of its undeclared war on the United States.
Now the uncertainties caused by the Russian attack on the Ukraine and corresponding energy supply shocks across Europe (who are more dependent on Russian oil) is fueling higher oil and gas profits and prices for consumers, further adding to inflationary fears born out of an uncertain Covid-impacted global supply chain system.
One year ago, President Biden called climate change “the number one issue facing humanity.” Alongside other world leaders, he made a slew of ambitious pledges to mitigate the use of fossil fuels and transition to renewable energy sources. A year later, the economic consequences of war on consumer energy costs has once again threatened progress in a global transition to a world operating within a sustainable and clean energy economy, and perhaps a final cure of world’s oil and gas addiction.
An energy addiction Hawaii must break
The cause and effect of regional wars inevitably effect the price of crude, often regionally, and less often on a global scale, as the current Ukrainian war has demonstrated by sending oil prices, already roiled by rising inflation, well over $150 a barrel range.
In addition to increasing the pain at the pump as gas prices rise, Hawaii will see electric bills increase substantially in the coming months following an outright ban on the U.S. import of Russian oil, natural gas and coal amid Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Hawaii’s state utility regulations require that the cost of fuel required for electricity generation be passed onto ratepayers. In short, be prepared for a significant increase in Hawaiian Electric energy bills.
The energy price shocks and impact will be less so for our friends in Kauai whose local utility, KUIC, is much more dependent on the Sun than Russian oil for delivering power to their customers.
Hawaiian Electric Co. Senior Communications Consultant Kristen Okinaka explained the utility’s outlook this way … “Over the next several months, we could be seeing a bill increase of up to 20% on Hawaii Island. As the U.S. and other nations stand with the people of Ukraine and impose powerful economic sanctions on Russia, including the refusal to buy Russian oil, Hawaii will see higher prices at the gas pump and in electric bills.”
Is the Cure Worse than the Disease
Department of Energy (DOE) Secretary Jennifer Granholm speaking Tuesday at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory’s national energy storage summit, made comments about the importance of shoring up battery and EV manufacturing and supply chains as a way to accelerate the clean energy transition and ensure energy independence for the United States, made two points that effectively counter the panic arguments of Big Oil’s agents that the US must throw caution-to-the-wind and double down on gas and oil extraction, production, and consumption — in short, feed the beast.
Granholm added, “Clean energy offers us a better way forward, and the only way to get closer to true energy independence [and] national security is by building out the technology at home with a reliable supply chain. “Nobody has ever held a country hostage over access to the sun or access to the wind.“
Hawaii’s biomass advocates of burning trees and trash for energy purposely fail to recognize the environmental, climate, and health consequences of fuel-combustion as means of generating electricity. Far from the proven zero emissions energy options now available, biomass energy combustion, even when fossil fuels are not involved, represent a dead end path to Hawaii’s clean energy future.
When fuels are burned, the stored carbon and other greenhouse gases are released into the atmosphere. An excess buildup of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has caused dramatic changes to Earth’s climate—a trend that will worsen as more fossil fuels are burned on top of 150 years of accumulated levels of GHG emissions, now stored in the Earth’s oceans, forests, and atmosphere.
Scientific and health organizations correctly defined the public health consequences conventional biomass options this way…
“Biomass is far from “clean” – burning biomass creates air pollution that causes a sweeping array of health harms, from asthma attacks to cancer to heart attacks, resulting in emergency room visits, hospitalizations, and premature deaths.”*
*The Allergy & Asthma Network, American Academy of Pediatrics, American Lung Association, American Public Health Association, Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America, National Association of County & City Health Officials, National Environmental Health Association, and Physicians for Social Responsibility.
Currently, we have a cadre of local fossil fuel and biofuel stakeholders whose financial interests lay squarely with Hawaii’s fossil fuel future, continue to view the world through a distorted lens closely aligned with energy replacements for coal, oil, and diesel, but which carry with them the energy production-combustion liabilities of greenhouse emissions and polluting byproducts.
Biomass advocates of these same so-called firm energy alternatives to solar, wind, and storage ignore history and brush aside the proven track record of reliability and cost-performance available today with zero emissions on-demand energy options. They position their “firm” energy arguments as “reliable” energy alternatives to fossil fuels, and ignore the environmental and climate consequences and costs of these so-called “firm” energy alternatives.
Taking an uncertain energy path of so-called “firm energy” alternatives to proven solar, wind, and energy storage options available now may produce less fossil fuel consumption burned for electricity production, but it will also deliver two significant certainties on the path to Hawaii’s acclaimed “clean energy” future; higher energy costs for our island communities, and a lost opportunity to fully address environmental-climate consequences plaguing our island state and the world today.
The role of the state’s largest utility
Hawaiian Electric is not unique within the utility community who view their rooftop solar customers as power-provisioning competitors. But world events have shaken this self-serving view, the power circumstances on Oahu have dramatically change with the long-awaited and mandated shut-down of Hawaii’s only coal-fired powerplant, AES, scheduled for this September.
The utility recently announced, and none too soon, that it will offer Oahu households with rooftop solar and batteries an option to aggregate up to 50 megawatts of capacity during peak consumption hours — a rare moment of collaborative outreach for Hawaiian Electric driven by desperation by tapping into its highly underappreciated energy asset, its rooftop solar customers. It was a good start for what should be an on-going and collaborative business model available in all energy markets HE serves, and one that serves the interests of both energy consumers and producers. Hawaiian Electric claims to also be pursuing a new 20-megawatt battery project and energy-conservation measures – details to follow.
Yes, an “economic” war with Russia is indeed a wake-up call to all that now is the time to complete the transition off our 20th century energy legacy and its unsustainable and a consequential addiction to fossil fuels.
Or we can put our heads in the sand, and wishfully believe we can continue in our 150 years of a dirty energy dependency, now needed more than ever in light of local and global events which are turning our world energy dependency and assumptions upside down.
Addendum
The winners in this titanic battle for survival in a fossil-free fuel world; the United States and the free-world. The losers, vested global fossil fuel interests, and the biggest fossil fuel companies in the world, and annual beneficiaries to some of the over $ Six Trillion USD in global taxpayer subsidies —
- Saudi Arabian Oil Co. ( Saudi Aramco)
- Revenue (TTM): $1.3 trillion
- Net Income (TTM): $330.3 billion
- Market Cap: $7.5 trillion
- Exxon Mobil Corp. ( XOM)
- Revenue (TTM): $280.4 billion
- Net Income (TTM): $23 billion
- Market Cap: $325.4 billion
TotalEnergies SE (TOT)
- Revenue (TTM): $184.6 billion
- Net Income (TTM): $16 billion
- Market Cap: $146.4 billion
- PetroChina Co. Ltd. ( PTR)*
- Revenue (TTM): $367 billion
- Net Income (TTM): $13 billion
- Market Cap: $95.8 billion
- China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. ( SNP)*
- Revenue (TTM): $353.2 billion
- Net Income (TTM): $14.3 billion
- Market Cap: $62.3 billion
Chevron Corp. (CVX)
- Revenue (TTM): $155.6 billion
- Net Income (TTM): $15.6 billion
- Market Cap: $261.3 billion
- British Petroleum PLC (BP)
- Revenue (TTM): $157.7 billion
- Net Income (TTM): $7.6 billion
- Market Cap: $101.6 billion
- Rosneft (JSC)
- Rosneft is Russia’s biggest integrated oil and gas company, generating $111.9 billion in revenue during 2019, producing 5.8 million barrels of oil per day
- The majority of its oil production takes place in Russia, but the company also has ongoing exploration and production activities in Canada, Vietnam, Norway, and Brazil, among other countries.
- Prior to its initial public offering (IPO) in 2006, all of Rosneft’s shares were owned by the Russian government through its holding company JSC Rosneftegaz, and as of 2019, the government maintains control of 50% of the company’s stock.
BP is abandoning its stake in Russian oil giant Rosneft in an abrupt and costly end to three decades of operating in the energy-rich country, marking the most significant move yet by a Western company in response to Moscow’s invasion of Ukraine. Rosneft accounts for around half of BP’s oil and gas reserves and a third of its production and divesting the 19.75% stake will result in charges of up to $25 billion, the British company said, without saying how it plans to extricate itself.



 but at what price; a question only recently asked and answered, as the energy status quo has become increasingly unsustainable by any reasonable measurement.
but at what price; a question only recently asked and answered, as the energy status quo has become increasingly unsustainable by any reasonable measurement.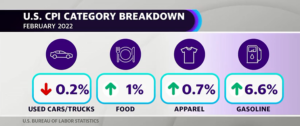 These impacts go well beyond the price of groceries or a tank of gas, and extend into agricultural productivity.. damages caused by sea level rise (presently about 40% of the world’s population lives within 50 miles of an ocean coastline).. environmental destruction on a global scale.. a decline in human health and labor productivity — and even this is a limited measurement of the impacts on humans and the planet economists use to determine CPI and other economic benchmarks to measure to the full weight and cost of our current fossil fuel dependency.
These impacts go well beyond the price of groceries or a tank of gas, and extend into agricultural productivity.. damages caused by sea level rise (presently about 40% of the world’s population lives within 50 miles of an ocean coastline).. environmental destruction on a global scale.. a decline in human health and labor productivity — and even this is a limited measurement of the impacts on humans and the planet economists use to determine CPI and other economic benchmarks to measure to the full weight and cost of our current fossil fuel dependency.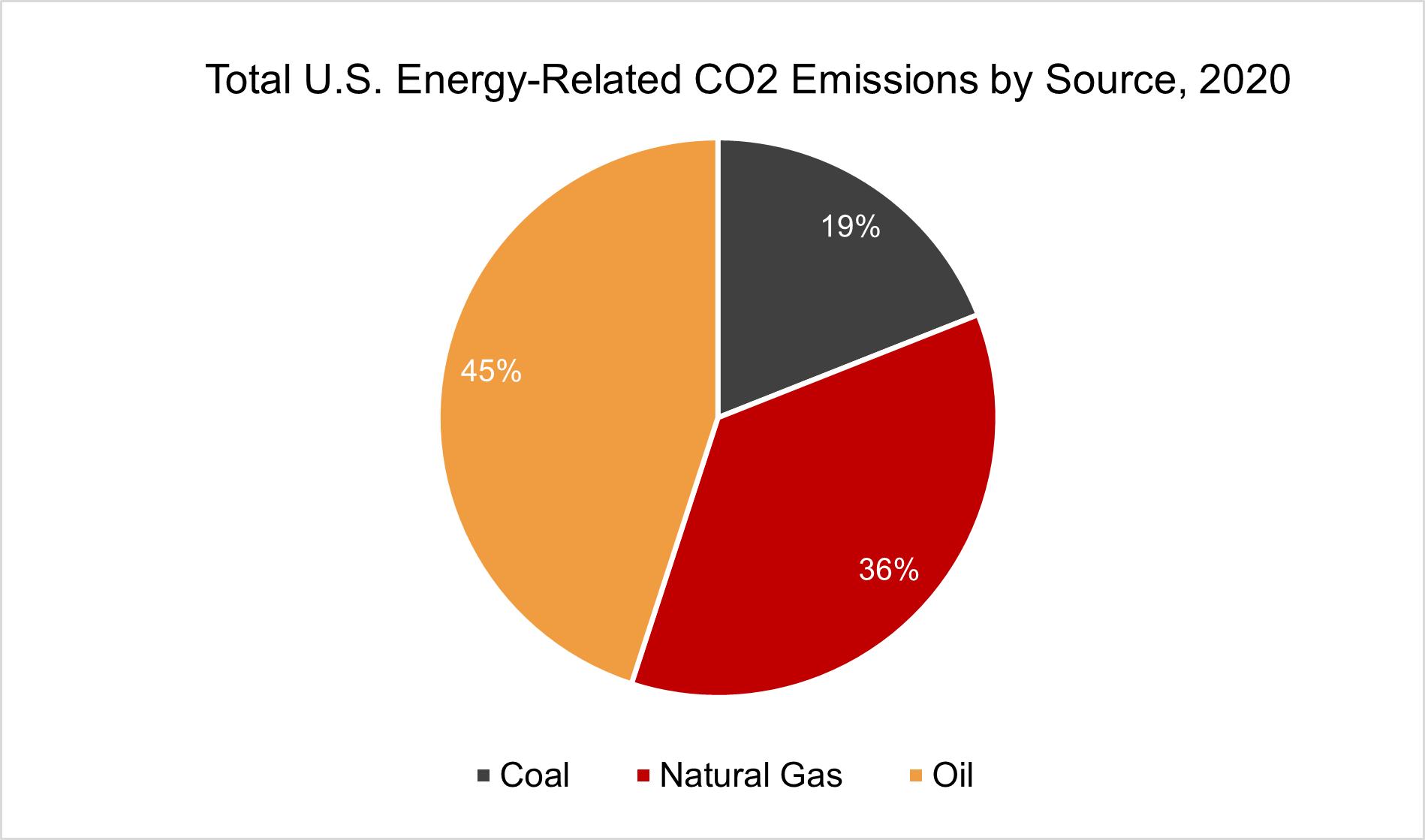






 In the case of the iFarm system, the company claims electricity consumption is divided into LED lamps (65%), air conditioners (20%) and dehumidifiers (10%) – which accounts for 95% of electricity usage, while the remaining devices use less than 5%. No total kWh power consumption comparisons to production examples were provided by the company.
In the case of the iFarm system, the company claims electricity consumption is divided into LED lamps (65%), air conditioners (20%) and dehumidifiers (10%) – which accounts for 95% of electricity usage, while the remaining devices use less than 5%. No total kWh power consumption comparisons to production examples were provided by the company. Organic farming, put simply, is returning organic matter to the soil so that the life in the soil cycles nutrients back to the crop. Highly soluble fertilizers kill much of the life in the soil, whereas organic matter feeds it. Organic farming is much more closely aligned with Hawaii’s traditional (non-corporate) farming practices. Organic produce, for example, merits a premium price in the retail store sales and higher profits for organic farmers.
Organic farming, put simply, is returning organic matter to the soil so that the life in the soil cycles nutrients back to the crop. Highly soluble fertilizers kill much of the life in the soil, whereas organic matter feeds it. Organic farming is much more closely aligned with Hawaii’s traditional (non-corporate) farming practices. Organic produce, for example, merits a premium price in the retail store sales and higher profits for organic farmers.