What’s in the bipartisan infrastructure bill for Hawaii
<August 10th, 2021>  The Senate gave overwhelming bipartisan approval to a $1 trillion infrastructure bill on Tuesday to rebuild the nation’s deteriorating roads and bridges and fund new climate resilience and broadband initiatives, delivering a key component of President Biden’s agenda.
The Senate gave overwhelming bipartisan approval to a $1 trillion infrastructure bill on Tuesday to rebuild the nation’s deteriorating roads and bridges and fund new climate resilience and broadband initiatives, delivering a key component of President Biden’s agenda.
It would provide historic levels of funding for the modernization of the nation’s power grid and projects to better manage climate risks, as well as pour hundreds of billions of dollars into the repair and replacement of aging public works projects.
To win the compromise, Democrats and Mr. Biden — who had initially proposed a $2.3 trillion infrastructure plan — had to make major concessions.
The package includes far less funding than they had wanted for lead pipe replacement, transit and clean energy projects, among others. But the result was passage of a crucial component of the president’s far-reaching, $4 trillion economic agenda.
But the measure now faces a potentially rocky and time-consuming path in the House, where the speaker, Nancy Pelosi, and the nearly 100-member Progressive Caucus, have said they will not vote on it unless and until the Senate passes a separate, even more ambitious $3.5 trillion social policy bill this fall.
<Originally published August 4th, 2021>
Analysis …
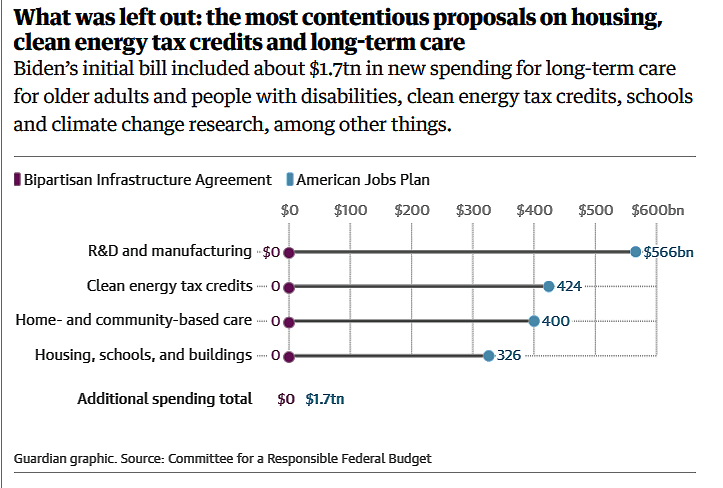
The good news — the bipartisan infrastructure bill maintains a large portion of President Biden’s proposals for roads, public transit and high-speed internet.
The bad news – this same bipartisan infrastructure bill has major funding holes in some key investment areas.
 The infrastructure bill with limited GOP participation was never designed properly address a a desperately needed national climate change response, instead developed into a bipartisan political grab bag of vital national 21st century investments, while upholding old economy, fossil fuel profit priorities.
The infrastructure bill with limited GOP participation was never designed properly address a a desperately needed national climate change response, instead developed into a bipartisan political grab bag of vital national 21st century investments, while upholding old economy, fossil fuel profit priorities.
In this scaled down bipartisan infrastructure version, Democrats were able to maintain a $7.5B investment for national EV charging system in the form of an EV/alternative fuel national fueling system, which is not necessarily designed to enable the Biden Administration’s goal of national build out of 500,000 additional electric vehicle charging stations.
The final bill language also contains a provision $3B for battery material processing grants + $3 billion for battery manufacturing and recycling grants.
The trick will be how this portion of the $7.5 billion in infrastructure investment (part 1) is allocated over the next few years. No doubt, the Biden administration will do its best ensure that goal is met.
Competing interests will make all the difference how the federal infrastructure investment dollars spent and distributed: a national EV charging system — or a hodgepodge build out of petro-sourced hydrogen, propane and natural gas fueling stations — GOP’s bill-participation nod to their Gas Oil Pollution patrons.
The tug of war for these dollars is just beginning. The results of the 2022 election cycle will play major role in how quickly America addresses a global climate crisis and transitions to a clean energy economy.
All this just in the Big Infrastructure Deal. However, more is needed after decades of infrastructure neglect and denial of a global climate threat of our own making which changed traditional views of infrastructure preparedness. In short, the bipartisan bill leaves much of the nation’s problems to the forthcoming American Jobs Plan to address and reconcile.
Bipartisan Infrastructure Recap:
Energy / Climate / Broadband
Power Grids: $27.65B for grid infrastructure, resiliency & reliability
This means connecting a lot more clean electricity to places that need it. Including $2.5B revolving loan fund from DOE for new transmission & upgrades + $3B for Smart Grid investments. For the mainland, the bill also provides leeway for DOE to designate corridors of nat’l interest & FERC ability to issue construction permits for some interstate transmission if states withhold/deny applications. Big step to address challenges w/ transmission.
$8.3B has been allocated to fund vital innovation programs from the Energy Act of 2020. This includes: demonstrations of energy storage, advanced nuclear, carbon capture, wind, solar, geothermal, and industrial emissions reduction, and a prize competition for direct air capture of CO2 emissions.
DAC or Direct Air Capture is new a technology area designed lower global CO2 levels in the atmosphere by first removing and then safely storing CO2 for the long term. The $3.5B is allocated for 4 direct air capture (DAC) hubs. Hubs can unite DAC facilities with industrial consumers and storage sites to remove and keep CO2 out of the atmosphere. A technology with huge, unfilled potential in addressing global warming emissions.
$8B has been also allocated to establish 4 regional hubs for clean hydrogen production, transport and use. This investment can help clean H2 industry take off. Another $500M has been allocated to establish and support a domestic supply chain for the production of clean H2 (without fossil fuels), and additional $1B demonstration project, designed to bring down the cost of H2 produced by electrolysis (green hydrogen).
$40B to deploy broadband to unserved areas, and the continuation of the affordability program to help low-income families.
Transportation
$39.15B in public transit: A 83% increase for transit over FAST Act.
This includes $8B for new transit construction/expansion, money that will help Hawaii address its inadequate, island-by-island, road system. Also included, $5.25B for Low/No emissions public transportation, and fleet wide transitions to clean, zero emissions buses.
“When I say electric vehicles are the future, I’m not joking,” tweeted President Biden. $7.5B investment for national EV charging system in the form of an EV/alternative fuel national transportation fueling system has been included in the bill — see above for further analysis and details.
$3 billion for battery material processing grants, and another $3 billion for battery manufacturing and recycling grants. An area of investment which applies both to EV’s and the renewable energy sectors. These kinds of investments are needed to spur domestic industry and reduce dependence on global competitors.




Leave a Reply
Join the Community discussion now - your email address will not be published, remains secure and confidential. Mahalo.